Calculating complicated circuits involves both series and parallel connections which is the reason why it is very important for you to have good analysis and mathematical understanding.
On this post let’s discuss about how to simplify an electronic circuit by providing you some basic examples.
On the example shown below, we have two resistor components that are connected in parallel. They are the R1 and R2 but they can be simplified into just one single resistor which we can derive as the R3.
This is how it can be done,
With this formula, we can now derive R3 with just a few simple mathematical transpositions.
Note:
The calculated value of the R3 should always be smaller than the R1 and R2 resistors.
On the example shown below, we have two resistor components that are connected in parallel. They are the R1 and R2 but they can be simplified into just one single resistor which we can derive as the R3.
This is how it can be done,
With this formula, we can now derive R3 with just a few simple mathematical transpositions.
Note:
The calculated value of the R3 should always be smaller than the R1 and R2 resistors.
As for the reason, parallel circuits do provide more paths for the electrical current to flow which causes the overall resistance of the circuit to be decreased.
For the Series connected resistors, they can as well be replaced by a single resistor just like the parallel but of different approach.
For the Series connected resistors, they can as well be replaced by a single resistor just like the parallel but of different approach.
On this example we have R1 and R2 that are connected in series connection. They can be combined which results as the R3 and this is how it can be done;
The formula is R3 = R1 + R2.
Note:
If the parallel connection tends to lower the total output resistance of the circuit, the series connection is the complete opposite where the total output resistance will increase in value.
The formula is R3 = R1 + R2.
Note:
If the parallel connection tends to lower the total output resistance of the circuit, the series connection is the complete opposite where the total output resistance will increase in value.
It is logical that adding more resistors in series will accumulate more resistivity on the circuit.
So those are the two basic formulas for simplifying any Series or Parallel circuit. For complicated circuits, you need to analyze them carefully to derive the overall equivalent resistance value.
So those are the two basic formulas for simplifying any Series or Parallel circuit. For complicated circuits, you need to analyze them carefully to derive the overall equivalent resistance value.
If you have further questions or do have some part on this discussion that you aren’t able to understand then you may use the comment form below.

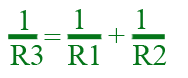


No comments:
Post a Comment